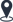
industry news5,industry news5industry news5industry news5industry news5
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery.[1] The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from which it exits.
Common uses include water, sewage, agriculture, petroleum, and petrochemical pumping. Centrifugal pumps are often chosen for their high flow rate capabilities, abrasive solution compatibility, mixing potential, as well as their relatively simple engineering.[2] A centrifugal fan is commonly used to implement an air handling unit or vacuum cleaner. The reverse function of the centrifugal pump is a water turbine converting potential energy of water pressure into mechanical rotational energy.
History
According to Reti, the first machine that could be characterized as a centrifugal pump was a mud lifting machine which appeared as early as 1475 in a treatise by the Italian Renaissance engineer Francesco di Giorgio Martini.[3] True centrifugal pumps were not developed until the late 17th century, when Denis Papin built one using straight vanes. The curved vane was introduced by British inventor John Appold in 1851.
Working principle
Cutaway view of centrifugal pump
Like most pumps, a centrifugal pump converts rotational energy, often from a motor, to energy in a moving fluid. A portion of the energy goes into kinetic energy of the fluid. Fluid enters axially through eye of the casing, is caught up in the impeller blades, and is whirled tangentially and radially outward until it leaves through all circumferential parts of the impeller into the diffuser part of the casing. The fluid gains both velocity and pressure while passing through the impeller. The doughnut-shaped diffuser, or scroll, section of the casing decelerates the flow and further increases the pressure.
Description by Euler
A consequence of Newton's second law of mechanics is the conservation of the angular momentum (or the “moment of momentum”) which is of fundamental significance to all turbomachines. Accordingly, the change of the angular momentum is equal to the sum of the external moments. Angular momentums
 Site Map
Site Map Contact
Contact leave a message
leave a message


